Applications of Fluid Mechanics Presentation Assaignment
Definition of Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids and the forces on them. It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, civil, chemical and biomedical engineering, geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology.
Classification of Fluid Mechanics
•Ideal
fluid
Ideal fluid is basically defined as a fluid which will be incompressible and in which viscosity will be zero.If we talk practically, there will be no existence of ideal fluid and therefore ideal fluid is an imaginary fluid only
•Real
Fluid
Real fluid is basically defined as a fluid which will be incompressible and in which
viscosity will not be zero. There will be viscosity in such fluids
•Example:•Water, Kerosene, Petrol, Air
Classification of Fluid Mechanics
Newtonian fluid
Newtonian fluid is basically defined as a fluid in which shear stress will be directly proportional with the velocity gradient.We can also say that a fluid which follows the Newton’s law of viscosity will be termed as Newtonian fluid.
Example:
Water, Air, Benzine etc
Non- Newtonian fluid
Non- Newtonian fluid is basically defined as a fluid in which shear stress will not be directly proportional with the rate of shear strain or velocity gradient.We can also say that a fluid which does not follow the Newton’s law of viscosity will be termed as Non- Newtonian fluid.
Example:
Plaster, Flubber, Slurries and Pastes etc.
Classification of Fluid Mechanics
Ideal Plastic fluid
Ideal Plastic fluid is basically defined as a fluid in which shear stress will be more than the yield value and shear stress will be directly proportional with the rate of shear strain or velocity gradient.
Incompressible fluid
If density of a fluid will not be changed with change in external pressure or force, then that fluid will be termed as Incompressible fluid. Liquids will be considered as incompressible fluid. Therefore, hydraulic accumulators are used to develop the nature of compressibility in hydraulic systems.
Classification of Fluid Mechanics
Compressible fluid
If density of a fluid will be changed with change in external pressure or force, then that fluid will be termed as compressible fluid. Gases will be considered as compressible fluid.
Applications of Fluid Mechanics in CE
Cranes
Elevators
Pipelines
Water Flow Under Lands
Geophysics
Oceanography
Applications of Fluid Mechanics in CE
Meteorology
Astrophysics
Hydrostatistics
Towers and Buildings
Water Distribution
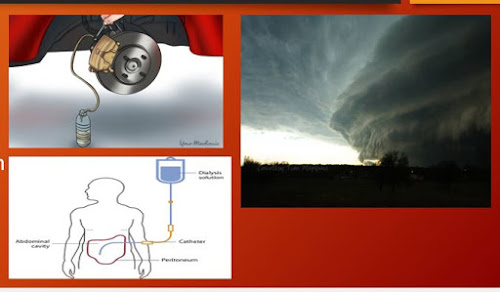
Braking System
Medical etc.















No comments