Direct Shear Test Of Metal Specimens Lab Report CE 213
DIRECT SHEAR
TEST OF METAL SPECIMENS
1.
OBJECTIVES
-To make a shear of metal
specimens approximating the conditions of shear existing in rivets, pins, and
bolts
-To determine the strength in single
and double shear
-To observe the shape and texture of
the fractured surface.
2.
APPARATUS AND MACHINE
UTM, shear tool, Slide calipers,
stop watch and computer.
3.
SIGNIFICANCE
This experiment provides
fundamental knowledge on direct shear behaviour of materials, test procedure,
universal testing machine and its working principal, specimens, failure
patterns etc.
4. SPECIMENS Steel
screws.
5. THEORY
Shearing stress is one that
acts parallel or tangential to stressed surface. It is different from normal
stress that acts perpendicular to the stressed surface, e.g. tension,
compression or bending stresses. It resists the tendency of a part of the body
on one side of the plane to slide against the other side of the same plane.
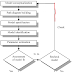
The
direct shear test (also called transverse shear test) gives an approximation to
the correct values of shearing strength. This test is usually done in a Johnson
type shear (Figure
1)
of shear tool by clamping a portion
of a material so that bending stress are minimized across the plane along which
the shearing load is applied. Because of inevitable bending and friction
between parts of tool, it gives an indication of the shearing resistance of materials.
The direct shear test has further limitation for the determination of elastic
strength or of the modulus of rigidity or shear rigidity, because of difficulty
to measure shearing strain.
6. PROCEDURE
i)
Measure the diameter of the specimen with the slide
calipers.
ii)
Fix the specimen in the shear tool
such that it is in single shear and apply load until rupture takes place.
iii) In the same
way test the specimen for double shear.
7. SAMPLE
CALCULATIONS
Calculate
double, unit double and single shear stresses from maximum shear force data.
8. GRAPH
1. Combined
Double Shear, Unit Double Shear and Single Shear force vs. displacement graph.
9. RESULT
|
|
Type of |
Dia |
Shear |
Maximum
Shear |
Maximum |
Failure |
Fracture |
|
|
|
Shear |
|
Area |
force |
Shear
stress or |
pattern |
surface |
|
|
|
|
|
(mm2) |
|
Shear
strength |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(mm) |
(N) |
(MPa) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Double |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.
DISCUSSION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(Discuss on the results found,
graphs, and failure patterns and also compare the results found, graphs and
failure patterns.)
Point
out the discussion
1.
2.
3.
….
11.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Why single
shear strength is greater than unit double shear?
2. How we can
measure shear rigidity?










No comments